Table of contents
Beans are a staple ingredient in cuisines worldwide, known for their versatility, nutritional value, and ability to enhance a variety of dishes. Among the many types of beans available, pinto beans and cranberry beans often spark curiosity. While they may look similar at first glance, they are not the same.
Understanding Pinto Beans
Pinto beans are one of the most popular bean varieties in North and South America. Known for their light brown color and speckled appearance, they’re a versatile and nutritious ingredient that can adapt to a wide range of culinary styles.
Origin of Pinto Beans
Pinto beans are believed to have originated in Central and South America, where they’ve been cultivated for thousands of years. The word “pinto” translates to “painted” in Spanish, a nod to their distinctive mottled appearance. Today, they are a staple in Mexican cuisine and are commonly used in dishes like refried beans, chili, and burritos.
Nutritional Profile of Pinto Beans
Pinto beans are a powerhouse of nutrition, offering:
- Protein: A valuable plant-based protein source, especially for vegetarians and vegans.
- Fiber: High in dietary fiber, supporting digestive health and reducing cholesterol levels.
- Micronutrients: Rich in iron, magnesium, potassium, and folate, contributing to energy production, heart health, and more.
Taste and Texture of Pinto Beans
Pinto beans have a mild, earthy flavor with a creamy texture when cooked. This makes them an excellent choice for dishes where the beans need to absorb surrounding flavors, such as soups, stews, and casseroles.
Culinary Uses of Pinto Beans
Their versatility makes pinto beans a staple in many kitchens. Some popular uses include:
- Mexican Dishes: Refried beans and tacos.
- American Classics: Chili and cowboy beans.
- Soups and Stews: Pinto beans add bulk and nutrition to hearty meals.
- Side Dishes: Often seasoned with spices and served alongside rice.
Understanding Cranberry Beans

Cranberry beans, sometimes referred to as borlotti beans, are another versatile and flavorful bean variety. Their beautiful marbled appearance and unique taste make them a standout in many cuisines worldwide.
Origin of Cranberry Beans
Cranberry beans trace their roots back to Italy and other Mediterranean regions, where they’ve been a beloved ingredient for centuries. They are widely grown in Europe and the Americas today and are particularly popular in Italian and Portuguese cooking.
Nutritional Profile of Cranberry Beans
Like pinto beans, cranberry beans are rich in essential nutrients, including:
- Protein: A similar level to pinto beans, ideal for muscle repair and growth.
- Fiber: Helps in maintaining a healthy gut and stabilizing blood sugar levels.
- Vitamins and Minerals: Packed with B vitamins, manganese, and zinc.
Taste and Texture of Cranberry Beans
Cranberry beans offer a slightly nutty and sweeter flavor compared to pinto beans. Their texture is creamy but slightly firmer, making them an excellent addition to dishes that require distinct bean shapes, such as salads and pasta dishes.
Culinary Uses of Cranberry Beans
Cranberry beans are a versatile ingredient in the kitchen, and they shine in:
- Italian Cuisine: Minestrone soup, pasta e fagioli, and stews.
- Portuguese Dishes: Often used in hearty, bean-rich recipes.
- Side Dishes: Sautéed with garlic, olive oil, and fresh herbs.
- Cold Salads: Their firmness makes them ideal for bean salads.
Comparing Pinto Beans and Cranberry Beans
While pinto beans and cranberry beans are both nutrient-rich legumes that share similarities, they differ in various aspects. Let’s dive deeper into their distinctions to clarify whether they can be used interchangeably or if they serve unique culinary purposes.
Physical Characteristics
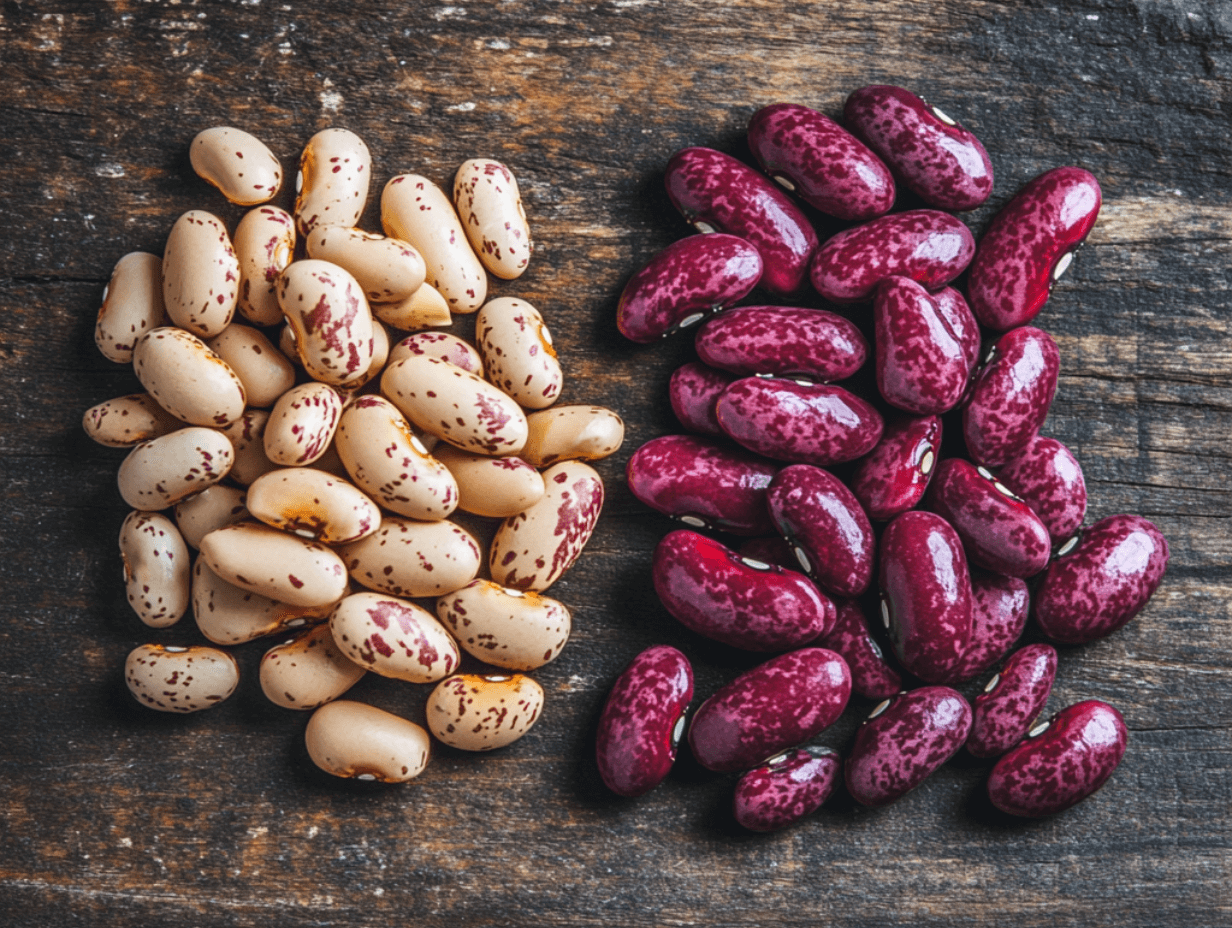
Appearance:
- Pinto beans are light brown with dark brown streaks, giving them a speckled look. When cooked, they lose much of their mottling and take on a uniform beige color.
- Cranberry beans are cream-colored with reddish or magenta streaks, creating a striking marbled pattern. Unlike pinto beans, their vibrant markings largely fade when cooked, leaving a pale or beige tone.
Size and Shape:
- Pinto beans are slightly smaller and more oval-shaped.
- Cranberry beans tend to be slightly larger and rounder, making them more visually distinct.
Taste and Texture
- Pinto Beans: Their mild, earthy flavor and creamy texture allow them to blend seamlessly into heavily seasoned dishes.
- Cranberry Beans: Known for their nutty and subtly sweet flavor, cranberry beans are often highlighted in recipes where their taste can shine. Their texture is creamy but firmer than pinto beans.
Nutritional Comparison
Both beans are rich in essential nutrients but offer slight variations:
- Protein: Comparable amounts, making both ideal for plant-based diets.
- Fiber: Both are excellent sources, but cranberry beans may have a slight edge in total fiber content.
- Vitamins and Minerals: Pinto beans provide higher levels of folate and magnesium, while cranberry beans are richer in manganese and certain antioxidants.
Culinary Applications
Substitution Possibilities:
- Pinto beans are excellent in dishes like refried beans or chili, where their creamy texture is essential.
- Cranberry beans are better suited to recipes that showcase their nutty flavor, such as bean salads, Italian soups, or simple sautés.
Versatility:
- Both beans work well in soups, stews, and casseroles, but their unique flavor profiles mean they shine in different cuisines. Pinto beans excel in Mexican and Tex-Mex dishes, while cranberry beans often feature in Italian and Mediterranean cooking.
Cost and Availability
Pinto beans are widely available and are often more affordable, especially in North America. Cranberry beans, while accessible, may be pricier and less commonly stocked in some regions.
Are Pinto Beans and Cranberry Beans Interchangeable?
While pinto beans and cranberry beans can sometimes be swapped in recipes, the results may vary depending on the dish:
When Substitution Works
- In soups and stews, where the beans absorb the surrounding flavors, either type can work well.
- For dishes that rely on the creamy texture of cooked beans, such as purees or dips, both are acceptable substitutes.
When Substitution Fails
- For recipes that emphasize the distinct flavor of cranberry beans, such as a bean salad or lightly seasoned Italian dishes, pinto beans might lack the nuanced sweetness and nuttiness required.
- If the appearance of the beans is crucial, as in cold dishes or side salads, the unique marbling of cranberry beans may be irreplaceable.
Tips for Substituting Beans
- Adjust seasonings to compensate for the flavor differences.
- Consider the texture and cooking time, as cranberry beans may remain firmer than pinto beans when cooked.
- Experiment with smaller portions to determine the best fit for your dish.
Health Benefits of Pinto Beans and Cranberry Beans
Both pinto beans and cranberry beans are nutrient-dense foods that offer a wide range of health benefits. While they share some similarities in their nutritional profiles, each bean also has unique attributes that contribute to their value in a healthy diet.
Shared Health Benefits
Both beans are excellent sources of essential nutrients that support overall health:
- Rich in Fiber: Both pinto and cranberry beans are high in dietary fiber, which promotes healthy digestion, supports weight management, and helps maintain stable blood sugar levels.
- Plant-Based Protein: They provide significant amounts of protein, making them ideal for vegetarians, vegans, or anyone looking to reduce their meat consumption.
- Heart Health: Low in fat and cholesterol, these beans are great for supporting cardiovascular health. Their potassium content also helps regulate blood pressure.
- Low Glycemic Index: Both beans release energy slowly, which is beneficial for people with diabetes or those looking to manage their blood sugar levels.
Unique Benefits of Pinto Beans
- Higher in Folate: Pinto beans are especially rich in folate, a B-vitamin crucial for cell growth, making them beneficial for pregnant individuals and those at risk of anemia.
- Magnesium Boost: Magnesium in pinto beans supports muscle function, nerve health, and bone strength.
- Weight Management: With a slightly lower calorie count per serving than cranberry beans, pinto beans can be helpful for those on a calorie-controlled diet.
Unique Benefits of Cranberry Beans
- Antioxidant Powerhouse: The pigments in cranberry beans, responsible for their reddish streaks, are rich in antioxidants, which combat oxidative stress and reduce inflammation.
- Manganese-Rich: Manganese in cranberry beans supports metabolism, bone health, and the body’s ability to heal wounds.
- Improved Gut Health: The higher fiber content of cranberry beans may promote healthier gut bacteria and better digestion compared to pinto beans.
Incorporating Beans into Your Diet
Adding pinto or cranberry beans to your meals is a simple way to enhance your diet:
- Soups and Stews: Both beans add bulk, flavor, and nutrients to brothy or thick stews.
- Salads: Cranberry beans shine in salads, where their firmness and color add visual and textural appeal.
- Mexican and Tex-Mex Dishes: Pinto beans are a classic in burritos, tacos, and enchiladas.
- Side Dishes: Either bean can be sautéed with olive oil, garlic, and herbs for a simple yet flavorful side.
Moderation and Allergies
While beans are incredibly nutritious, consuming them in moderation is essential:
- Digestive Concerns: Some individuals may experience bloating or gas due to the complex carbohydrates in beans. Soaking beans before cooking and consuming them in small portions can help.
- Allergies and Sensitivities: Though rare, some people may be allergic to legumes. If you’re trying beans for the first time, monitor for any adverse reactions.
Cooking Tips and Recipes
Cooking pinto beans and cranberry beans to perfection requires proper preparation and techniques. Both varieties are highly versatile and can be incorporated into a wide range of dishes. Whether you’re a novice cook or a kitchen pro, these tips will help you get the best results every time.
Preparing Pinto Beans and Cranberry Beans
- Soaking Beans:
- Soaking beans overnight reduces cooking time and helps make them easier to digest. Place the beans in a large bowl, cover with water, and let them sit for 8-12 hours.
- For a quicker option, use the “quick soak” method: boil the beans for 2 minutes, remove from heat, and let them sit in hot water for 1 hour before cooking.
- Rinsing:
- After soaking, drain and rinse the beans thoroughly to remove any dirt or debris.
- Cooking Tips:
- Cook beans in a large pot with fresh water. Bring to a boil, then reduce to a simmer.
- Add flavor enhancers like bay leaves, garlic, onions, or spices to the water, but avoid adding acidic ingredients (like tomatoes or vinegar) until the beans are fully cooked, as these can prevent softening.
- Cooking Time:
- Pinto beans: Approximately 1.5 to 2 hours on the stovetop.
- Cranberry beans: Slightly shorter cooking time, around 1 to 1.5 hours.
Popular Recipes with Pinto Beans
- Refried Beans:
- A classic Mexican dish made by mashing cooked pinto beans and frying them with onions, garlic, and spices. Serve as a side dish or use as a filling for burritos and tacos.
- Pinto Bean Chili:
- A hearty stew combining pinto beans with tomatoes, ground beef or turkey (optional), chili powder, and cumin. It’s perfect for cold evenings.
- Southern Pinto Beans:
- Slow-cooked with ham hocks or smoked sausage, onions, and spices, this dish is a flavorful comfort food.
Popular Recipes with Cranberry Beans

- Italian Borlotti Bean Stew:
- A flavorful dish with cranberry beans, tomatoes, garlic, and fresh herbs like rosemary and thyme. Serve with crusty bread for a complete meal.
- Cranberry Bean Salad:
- Combine cooked cranberry beans with chopped vegetables, olive oil, lemon juice, and fresh parsley for a refreshing and nutritious salad.
- Portuguese Feijoada:
- A traditional dish made with cranberry beans, pork, and spices, simmered into a rich and hearty stew.
Tips for Enhancing Bean Dishes
- Season Generously:
- Use bold spices, fresh herbs, and aromatics to boost the flavor of beans.
- Texture Balance:
- Mash some of the beans in soups or stews for a creamy texture while leaving others whole.
- Storage:
- Cooked beans can be stored in an airtight container in the refrigerator for up to 5 days or frozen for up to 3 months.
- Batch Cooking:
- Cook large quantities of beans at once and freeze portions to save time for future meals.
FAQs About Pinto Beans and Cranberry Beans
Can Pinto Beans and Cranberry Beans Be Used Interchangeably in All Recipes?
While both beans share similarities, their differences in flavor and texture make them more suitable for certain dishes. Pinto beans’ mild taste and creamy texture work well in refried beans, burritos, and chili, while cranberry beans’ nutty flavor and firmer texture shine in salads, Italian stews, and side dishes. Substitution is possible but may slightly alter the taste and presentation.
Are Pinto Beans and Cranberry Beans Equally Nutritious?
Both beans are nutrient-dense, offering protein, fiber, and essential vitamins. Pinto beans have slightly higher levels of folate and magnesium, beneficial for heart health and energy production. Cranberry beans, on the other hand, contain more antioxidants and manganese, supporting metabolism and combating oxidative stress.
How Should I Store Pinto Beans and Cranberry Beans?
- Dried Beans: Store in a cool, dry place in an airtight container. Properly stored dried beans can last up to 1 year or more without losing quality.
- Cooked Beans: Keep them in an airtight container in the refrigerator for up to 5 days or freeze for up to 3 months. Ensure beans are completely cool before storing.
Conclusion
Pinto beans and cranberry beans are both versatile, nutritious legumes, each with its unique flavor profile, texture, and culinary applications. While they may look similar at a glance, their differences become apparent when you dive into their taste, appearance, and nutritional benefits.
Pinto beans, with their creamy texture and mild flavor, are perfect for Mexican and Tex-Mex dishes, refried beans, and hearty stews. Cranberry beans, with their nutty taste and firmer texture, excel in Mediterranean dishes, salads, and elegant side dishes.